This page is important and should not be deleted.
Anyone doing so will have their adminship revoked and banned, depending on the importance of the page.
Google Maps is a web mapping platform and consumer application provided by Google. It offers satellite imagery, aerial photography, street maps, 360 degree interactive panoramic views of streets (Street View), real-time traffic conditions, and route planning for traveling by foot, car, air (in beta), and public transportation, As of 2020, Google Maps was being used by over 1 billion people every month around the world.
Google Maps began as a C++ desktop program developed by brothers Lars and Jens Rasmussen at Where 2 Technologies. In October 2004, the company was acquired by Google, which converted in into a web application. After additional acquisitions of a geospatial data visualization company and a real time traffic analyzer, Google Maps was launched in February 2005. The service's front end utilizes JavaScript, XML, and Ajax. It offers an API that allows maps to be embedded on third-party websites, and offers a locator for businesses and other organizations in numerous countries around the world. Google Map Maker allowed users to collaboratively expand and update the service's mapping worldwide but was discontinued from March 2017. However, crowdsourced contributions to Google Maps were not discontinued as the company announced those features would be transferred to the Google Local Guides program.
Google Maps' satellite view is a "top-down" or bird's-eye view; most of the high-resolution imagery of cities is aerial photography taken from aircraft flying at 800 to 1,500 feet (240 to 460 m), while most other imagery is from satellites. Much of the available satellite imagery is no more than three years old and is updated on a regular basis. Google Maps previously used a variant of the Mercator projection, and therefore could not accurately show areas around the poles. In August 2018, the desktop version of Google Maps was updated to show a 3D globe. It is still possible to switch back to the 2D map in the settings.
Google Maps for Android and iOS devices was released in September 2008 and features GPS turn-by-turn navigation along with dedicated parking assistance features.
In August 2013, it was determined to be the world's most popular smartphone app, with over 54% of global smartphone owners using it.
In May 2017, the app has reported to have 2 billion users on Android, along with several other Google services including YouTube, Chrome, Gmail, Search, and Google Play.
History[]
Acquisitions[]
Google Maps has its origins as a C++ program designed by two Danish brothers Lars and Jens Rasmussen, as well as Noel Gordon and Stephen Ma, created at the Australian company Where 2 Technologies. It was first designed to be separately downloaded by users, but the company later pitched the idea for a purely Web-based product to Google management, changing the method of distribution. In October 2004, the company was acquired by Google where it transformed into the web application Google Maps.
In the same month, Google acquired Keyhole, a geospatial data visualization company, whose marquee application suite, Earth Viewer, emerged as the highly successful Google Earth application in 2005 while other aspects of its core technology were integrated into Google Maps.
Google also acquired ZipDash, a company that provided real-time traffic analysis, in September 2004.
2005-2010[]
The launch of Google Maps was first announced on the Google blog on February 8, 2005.
In September 2005, in the aftermath of Hurricane Katrina, Google Maps quickly updated its satellite imagery of New Orleans to allow users to view the extent of the flooding in various parts of the city.
On November 28, 2007, Google Maps for Mobile 2.0 was released, which featured a beta version of a "My Location" feature that uses the GPS location of the mobile device supplemented by determining the nearest wireless networks and cell sites.
On September 23, 2008, coinciding with the announcement of the first commercial Android device, Google announced that a Google Maps app had been released for its Android operating system.
In October 2009, Google replaced Tele Atlas as their primary supplier of geospatial data in the US version of Maps and used their own data.
2011-2015[]
2016-2018[]
since 2019[]
Satellite view[]
Google Maps provides high-resolution aerial or satellite images for most urban areas all over the world. The current satellite imagery is over 5 years old, and thus not accurate in several places where urban architecture has been altered since. Various governments have complained about the potential for terrorists to use the satellite images in planning attacks.[1][dead link] Google has blurred some areas for security (mostly in the United States),[2] including the U.S. Naval Observatory area (where the official residence of the Vice President is located), and previously[3] the United States Capitol and the White House. Other well-known government installations, including Area 51 in the Nevada desert, are visible. Not all areas on satellite images are covered in the same resolution; less populated areas usually get less detail. Some areas may be obscured by patches of clouds.[4][5] With the introduction of an easily pannable and searchable mapping and satellite imagery tool, Google's mapping engine prompted a surge of interest in satellite imagery. Sites were established which feature satellite images of interesting natural and man-made landmarks, including such novelties as "large type" writing visible in the imagery, as well as famous stadia and unique geological formations. Although Google uses the word satellite, most of the high-resolution imagery of cities is aerial photography taken from aircraft flying at 800–1500 feet rather than from satellites; while most of the rest of the imagery is in fact from satellites.[6]
Although the aerial views images are undated, they occasionally coincide with known events. For example, as of Oct. 8, 2011, the aerial view of the Hollywood region of Los Angeles shows the street-closures and temporary structures related to the 2011 Academy Awards ceremony.
Directions[]

Contiguous regions on Google Maps
Google Maps provides a route planner under "Get Directions". Up to four modes of transportation are available depending on the area: driving, public transit (see the Google Transit section below), walking, and bicycling. In some areas, cross-border routes are available, whereas others are limited to routes within a given country or region. Driving directions are covered as follows:
- Most countries of mainland Eurasia and Africa are covered contiguously, including the United Kingdom, Ireland, the Canary Islands, Madeira and Sri Lanka. No directions are available for Bosnia and Herzegovina, North and South Korea, Lesotho and Oman; while China, Cyprus, Egypt, Hong Kong, Israel (including parts of the West Bank), Jordan, Lebanon, Macau and Malta have directions available without connection to other states.
- All countries of mainland North and Central America are covered contiguously.
- All countries of mainland South America are covered. Argentina, Bolivia, Brazil, Chile, Ecuador, Paraguay, Peru and Uruguay are treated contiguously, whereas Colombia, French Guiana, Guyana, Suriname and Venezuela are not connected to other states.
- All inhabited countries and territories in the Caribbean are covered, except for Saint Kitts and Nevis and Trinidad and Tobago, though in general there are no connections between islands.
- Additionally, American Samoa, Australia, the Azores, Brunei, Cape Verde, The Comoros, The Cook Islands, the Faroe Islands, The Federated States of Micronesia, Fiji, French Polynesia, Guam, Hawaii, Iceland, Japan, Madagascar, the Maldives, Mauritius, Mayotte, New Caledonia, New Zealand, Niue, Palau, the Philippines, Réunion, São Tomé and Príncipe, the Seychelles, Samoa, Taiwan, Timor-Leste, Tonga, Vanuatu, Wallis and Futuna are covered as stand-alone regions, as are Nuuk in Greenland, parts of Indonesia (Bali, Borneo, Java, Lombok, Madura, Sulawesi and Sumatra), Sabah and Sarawak in Malaysia, Saipan in the Northern Mariana Islands, parts of Papua New Guinea, parts of Solomon Islands and Socotra in Yemen.
In addition, only directions with public transit are provided in South Korea.
Implementation[]
Like many other Google web applications, Google Maps uses JavaScript extensively.[7] As the user drags the map, the grid squares are downloaded from the server and inserted into the page. When a user searches for a business, the results are downloaded in the background for insertion into the side panel and map; the page is not reloaded. Locations are drawn dynamically by positioning a red pin (composed of several partially transparent PNGs) on top of the map images.
A hidden IFrame with form submission is used because it preserves browser history. The site also uses JSON for data transfer rather than XML, for performance reasons. These techniques both fall under the broad Ajax umbrella.
In October 2011, Google announced MapsGL, a WebGL version of Maps with better renderings and smoother transitions.[8]
Extensibility and customization[]
As Google Maps is coded almost entirely in JavaScript and XML, some end users have reverse-engineered the tool and produced client-side scripts and server-side hooks which allowed a user or website to introduce expanded or customized features into the Google Maps interface.
Using the core engine and the map/satellite images hosted by Google, such tools can introduce custom location icons, location coordinates and metadata, and even custom map image sources into the Google Maps interface. The script-insertion tool Greasemonkey provides a large number of client-side scripts to customize Google Maps data.
Combinations with photo sharing websites, such as Flickr, are used to create "memory maps". [clarification needed What are memory maps?] Using copies of the Keyhole satellite photos, users have taken advantage of image annotation features to provide personal histories and information regarding particular points of the area.
Google Maps API[]
After the success of reverse-engineered mashups such as chicagocrime.org and housingmaps.com, Google launched the Google Maps API in June 2005[9] to allow developers to integrate Google Maps into their websites. It is a free service, and currently[update] does not contain ads, but Google states in their terms of use that they reserve the right to display ads in the future.[10]
By using the Google Maps API, it is possible to embed Google Maps site into an external website, on to which site specific data can be overlaid. Although initially only a JavaScript API, the Maps API has since expanded to include an API for Adobe Flash applications, a service for retrieving static map images, and web services for performing geocoding, generating driving directions, and obtaining elevation profiles. Over 350,000[11] web sites use the Google Maps API, making it the most heavily used web application development API.[12]
The Google Maps API is free for commercial use providing that the site on which it is being used is publicly accessible and does not charge for access, and is not generating more than 25 000 map accesses a day.[13][14] Sites that do not meet these requirements can purchase Google Maps API Premier.[15]
The success of the Google Maps API has spawned a number of competing alternatives, including the Yahoo! Maps API, Bing Maps Platform, MapQuest Development Platform, and OpenLayers.
In September 2011, Google announced it would discontinue a number of its products, including Google Maps API for Flash.[16]
Google Maps for Mobile[]
In 2006, Google introduced a Java application called Google Maps for Mobile, intended to run on any Java-based phone or mobile device. Many of the web-based site's features are provided in the application.[17]
On November 28, 2007, Google Maps for Mobile 2.0 was released. It introduced a GPS-like location service that does not require a GPS receiver. The "my location" feature works by utilizing the GPS location of the mobile device, if it is available. This information is supplemented by the software determining the nearest wireless networks and cell sites. The software then looks up the location of the cell site using a database of known wireless networks and cell sites. The Cell-site location method is used by triangulating the different signal strengths from different cell transmitters and then using their location property (retrieved from the online cell site database) to aid My Location in determining the user's current location. Wireless network location method is calculated by discovering the nearby WiFi hotspots and using their location property (retrieved from the online WiFi database, in the same way as the cell site database) to further discover the user's location. The order in which these take precedence is:
- GPS-based services
- WLAN-, WiFi-based services
- Cell transmitter-based services
The software plots the streets in blue that are available with a yellow icon and a green circle around the estimated range of the cell site based on the transmitter's rated power (among other variables). The estimate is refined using the strength of the cell phone signal to estimate how close to the cell site the mobile device is.
As of MM DD, YYYY[update], this service is available for the following platforms:[18]
- Android
- iOS (iPhone, iPod Touch, iPad)
- PlayStation Vita 3G Models
- Windows Mobile (NOT Windows Phone 7 as of MM DD, YYYY[update])
- Nokia/Symbian (S60 3rd & 5th edition only)
- Symbian OS (UIQ v3)
- BlackBerry
- Phones with Java-Platform (MIDP 2.0 and up), for example the Sony Ericsson K800i
- Palm OS (Centro and newer)
- Palm webOS (Palm Pre and Palm Pixi)
On November 4, 2009, Google Maps Navigation was released in conjunction with Google Android OS 2.0 Eclair on the Motorola Droid, adding voice commands, traffic reports, and street view support.[19] The initial release was limited to the United States.[20] The service was launched in the UK on 20 April 2010 and in large parts of continental Europe on June 9, 2010 (including Austria, Belgium, Canada, Denmark, France, Germany, Italy, the Netherlands, Portugal, Spain, and Switzerland).[21]
In March 2011, Google Vice President of Location Service, Marissa Mayer announced that Google provides map services to 150 millions users.[22]
In June 2012, Apple announced that they will be removing Google Maps on iOS 6 and would be replaced with their own maps service.
Google Maps Android 2.0[]
Google Maps for Android
Cell phones are being increasingly used for navigation assistance. Google Maps Navigation for Android 2.0 is free.
Features provided in the application:
- Search in plain English
- Search by voice
- Traffic view
- Search along route
- Satellite view
- Street View
- Car dock mode
Impact[]
Google Maps Navigation is free. A potential drawback of Google Maps for Android is that maps are not included in the application file. An internet connection is required to get maps and related information from Google Maps, just like with iPhone’s Google Maps application.[23] This drawback is mitigated by an automatic map caching feature which temporarily stores recently viewed areas. There is also a 'Download Map Area' feature in the Labs section of Google Maps. The 'Download Map Area' feature enables the user to download the road map and landmark data for an area of Template:Convert/ around any point. The user can do this action multiple times to cover as much area as desired. Google suggests that users can make use of this feature to download the map of a foreign city before traveling to visit it, so that once the user arrives in the city, they can refer to the pre-downloaded road map without needing to use expensive international roaming data. However, the downloaded map area only includes the basic road map and its landmark labels. Google notes that even after you download a map area, "you still need a data connection to see satellite view and 3D buildings, search for Places and get directions."[24]
Google Maps parameters[]
In Google Maps, URL parameters are sometimes data-driven in their limits and the user interface presented by the web may or may not reflect those limits. In particular, the zoom level (denoted by the z parameter) supported varies. In less populated regions, the supported zoom levels might stop at around 18. In earlier versions of the API, specifying these higher values might result in no image being displayed. In Western cities, the supported zoom level generally stops at about 20. In some isolated cases, the data supports up to 23 or greater, as in these elephants or this view of people at a well in Chad, Africa. Different versions of the API and web interfaces may or may not fully support these higher levels.
As of October 2010, the Google map viewer updates its zoom bar to allow the user to zoom all the way when centered over areas that support higher zoom levels.
History[]
Acquisition[]
Google Maps first started as a C++ program designed by two Danish brothers Lars and Jens Rasmussen at the Sydney-based company Where 2 Technologies. It was first designed to be separately downloaded by users but the company later pitched the idea for a purely Web-based product to Google management, changing the method of distribution.[25] In October 2004 the company was acquired by Google Inc[26] where it transformed into the web application Google Maps. The application was first announced on the Google Blog on February 8, 2005 at Midnight ET (February 7 technically it got launched followed by YouTube that has also required to launched within videos),[27] and was located at Google. It originally only supported users of Internet Explorer and Mozilla web browsers, but support for Opera and Safari was added on February 25, 2005, but currently[when?] Opera is removed from the system requirements list. As of 2010[update] Internet Explorer 7.0+, Firefox 3.6+, Safari 3.1+, and Google Chrome are supported.[28] It was in beta for six months before becoming part of Google Local on October 6, 2005.
2005[]
In April 2005, Google created Google Ride Finder using Google Maps. In June 2005, Google released the Google Maps API. In July 2005, Google began Google Maps and Google Local services for Japan, including road maps. On July 22, 2005, Google released "Hybrid View". Together with this change, the satellite image data was converted from plate carrée to Mercator projection, which makes for a less distorted image in the temperate climes latitudes. In July 2005, in honor of the thirty-sixth anniversary of the Apollo Moon landing, Google Moon was launched. In September 2005, in the aftermath of Hurricane Katrina, Google Maps quickly updated its satellite imagery of New Orleans to allow users to view the extent of the flooding in various parts of that city. (Oddly, in March 2007, imagery showing hurricane damage was replaced with images from before the storm; this replacement was not made on Google Earth, which still uses post-Katrina imagery).[29][30]
2006[]
From January 2006, Google Maps featured road maps for the United States, Puerto Rico, Canada, the United Kingdom, Japan, and certain cities in the Republic of Ireland. Coverage of the area around Turin was added in time for the 2006 Winter Olympics. On January 23, 2006, Google Maps was updated to use the same satellite image database as Google Earth. On March 12, 2006, Google Mars[31] was launched, which features a draggable map and satellite imagery of the planet Mars. In April 2006, Google Local was merged into the main Google Maps site. On April 3, 2006, version 2 of the Maps API was released.[32][dead link] On June 11, 2006, Google added geocoding capabilities to the API, satisfying the most developer-requested feature for this service.[33] On June 14, 2006, Google Maps for Enterprise was officially launched.[34] As a commercial service, it features intranet and advertisement-free implementations. In July 2006 Google started including Google Maps business listings in the form of Local OneBoxes in the main Google search results.[35] On December 9 Google integrates the PlusBox in the main search results.[36] On December 19 Google added a feature that lets you add multiple destinations to your driving directions.[37] Beginning in February 2007, buildings and subway stops are displayed in Google Maps "map view" for parts of New York City, Washington, D.C., London, San Francisco, and some other cities.[38]
2007[]
On January 29, 2007 Local Universal results were upgraded and more data included in the main Google results page.[39] On February 28, 2007, Google Traffic info was officially launched to automatically include real-time traffic flow conditions to the maps of 30 major cities of the United States.[40] On March 8, 2007, the Local Business Center was upgraded.[41] On May 16, 2007 Google rolled out Universal search results, including more Map information on the main Google results page.[42] On May 18, 2007 Google added neighborhood search capabilities.[43] On May 29, 2007, Google driving directions support was added to the Google Maps API.[44] On May 29, 2007, Street View was added, giving a ground-level 360-degree view of streets in some major cities in United States.[45] On June 19, 2007, reviews were allowed to be added directly to businesses on Google Maps.[46] On June 28, 2007, draggable driving directions were introduced.[47] On July 31, 2007, support for the hCard microformat was announced.[48] Unfortunately, the implementation is broken.[citation needed] On August 21, 2007, Google announced a simple way to embed Google Maps into other websites.[49] On September 13, 2007, 54 new countries were added to Google Maps in Latin America and Asia.[50] On October 3, 2007, Google Transit was integrated into Google Maps making public transportation routing possible on Google Maps.[51] On October 27, 2007, Google Maps started mapping the geoweb and showing the results in Google Maps.[52] On October 27, 2007, Google Maps added a searchable interface for coupons in the business listings.[53] On November 27, 2007, "Terrain" view showing basic topographic features was added. The button for "Hybrid" view was removed, and replaced with a "Show labels" checkbox under the "Satellite" button to switch between "Hybrid" and "Satellite" views.[citation needed]
2008[]
On January 22, 2008, Google expanded the Local Onebox from 3 business listings to 10.[54] On February 20, 2008, Google Maps allowed searches to be refined by User Rating & neighborhoods.[55] On March 18, 2008, Google allowed end users to edit business listings and add new places.[56] On March 19, 2008, Google added unlimited category options in the Local Business Center.[57] On April 2, 2008, Google added contour lines to the Terrain view.[58] In April 2008, a button to view recent Saved Locations was added to the right of the search field.[citation needed] In May 2008, a "More" button was added alongside the "Map", "Satellite", and "Terrain" buttons, permitting access to geographically related photos on Panoramio and articles on Wikipedia.[citation needed] On May 15, 2008, Google Maps was ported to Flash and ActionScript 3 as a foundation for richer internet applications.[citation needed] On July 15, 2008, walking directions were added.[59] On August 4, 2008, Street View launched in Japan and Australia.[59] On August 5, 2008, the user interface was redesigned.[59] On August 29, 2008, Google signed a deal under which GeoEye would supply them with imagery from a satellite,[60] and introduced the Map Maker tool, which allows any user to improve the map data seen by all.[59] On September 9, 2008, a reverse business lookup feature was added.[59] On September 23, 2008, information for the New York City Metropolitan Transit Authority was added.[59] On October 7, 2008, GeoEye-1 took its first image, a bird's-eye view of Kutztown University in Pennsylvania.[61] On October 26, 2008, reverse geocoding was added to the Maps API.[59] On November 11, 2008, Street View in Spain, Italy, and France was introduced.[59] On November 23, 2008, AIR support for the Maps API for Flash was added.[59] On November 25, 2008, a new user interface for Street View was introduced.[59] On November 27, 2008, maps, local business information, and local trends for China were introduced.[59] On December 9, 2008, 2x Street View coverage was introduced.[59]
2009[]
In May, 2009, a new Google Maps logo was introduced.[62] In early October 2009, Google replaced Tele Atlas as their primary supplier of geospatial data in the U.S. version of Maps and use their own data.[63] In October 2009, the railroads were redone, featuring a slightly new look and updated, removing older lines.[citation needed] Also in the same month, maps in several areas were changed to include paper streets and other odd roads that don't exist, as well as lot lines showing up on the map interface.[citation needed]
2010[]
On February 11, 2010, Google Maps Labs was added. On March 11, 2010, Street View in the United Kingdom, Hong Kong, Macau, and more locations in Japan were launched. On May 25, 2010, public transportation routing for Denmark was added by integrating with Rejseplanen.dk.[64]
2011[]
On April 8, Google announced they would begin charging for API usage by commercial sites over a limit.[65] They also introduced a premium licensed service.
On April 19, 2011, Map Maker was added to U.S. Google Maps. Google made its Map Maker feature available in the U.S., allowing any viewer to edit and add changes to Google Maps. This was done since Open Street Map updating was so successful. Basically Google can get local map updates almost in real time compared to waiting for digital map data companies which only release expensive updates monthly. Google saves money by first having workers in India do the checking, and second, having the general public do the edits they once paid a premium dollar for. And the added plus is the data is copyrighted and owned by Google once checked and added to their GIS database.
2012[]
On January 31, 2012, Google was found guilty of abusing the dominant position of its Google Maps application and ordered by a court to pay a fine and damages to Bottin Cartographes, a French mapping company.[66]
On May 30, 2012, Google Places was replaced by Google+ Local, which now integrates directly with the Google+ service to allow users to post photos and reviews of locations directly to its page on the service. Additionally, Google+ Local and Maps also now feature detailed reviews and ratings from Zagat, who was acquired by Google in September 2011.[67]
In June 2012, Google started mapping Britain's rivers and canals in partnership with the Canal and River Trust. This feature will allow customers to plan trips including locks, bridges, and towpaths along 2,000 miles of rivers in the UK.
Local Guides[]
Overview[]
Local Guides is a global community of explorers who write reviews, share photos, answer questions, add or edit places, and check facts on Google Maps. Millions of people rely on contributions like yours to decide where to go and what to do.
Become a Local Guide[]
Sign up with your Google account and select your current location. Every place you review, photograph, add, edit, or provide additional info for on Google Maps earns you points toward unlocking something new.
Who can be a Local Guide[]
Local Guides is offered everywhere Google Maps is available. At this time, Google Maps is available in more than 40 countries and languages.
The Local Guides program is for individuals, not businesses. Contributions from businesses or business pages will not count toward Local Guides levels or benefits.
You must be 18 years* or older to participate in Local Guides. For more information, review the Local Guides Program Terms and Conditions.
*Note: it may take up to 9 weeks after you turn 18 for your Google account to update.
Watch this video to learn more: https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=oTspwtBMjdo&feature=emb_logo
Points, levels, and badging[]
Local Guides points[]
Earn points by contributing content to Google Maps. Score a place with ratings, describe your experience with reviews, share photographs and videos, provide insights with answers, respond to questions about a place, update information with place edits, add missing places, or verify information by checking facts.
| Maps contribution | Points earned |
|---|---|
| Review | 10 points per review |
| Review with more than 200 characters | 10 bonus points per review |
| Rating | 1 point per rating |
| Photo | 5 points per photo |
| Photo tags | 3 points per tag |
| Video | 7 points per video |
| Answer | 1 point per answer |
| Respond to Q&As | 3 points per response |
| Edit | 5 points per edit |
| Place added | 15 points per place added |
| Road added | 15 points per road added |
| Fact checked | 1 point per fact checked |
| Eligible list published | 10 points per published list |
| Description (in list) | 5 points per description added |
Local Guides levels[]
Reach higher levels as you earn points for your contributions.
Please note your points and level can take up to 24 hours to update. Points do not expire, though they may decrease if content is removed for violating the Google policies. Remain an active contributor on Google Maps to be eligible for perks and early access to new features.
Google's use of Google Maps[]
Google Ditu[]
Google Ditu (谷歌地图 lit. "Google Maps") was released to the public on February 9, 2007, and replaced the old Google Bendi (谷歌本地 lit. "Google Local"). This is the Chinese localized version of Google Maps and Google Local services.
In order to be compliant with the requirements of Chinese law, Google had to remove or modify some Google Maps features in Google Ditu:
- Google Ditu does not allow overlay of user-generated content from Panoramio, YouTube, Wikipedia and webcams.
- Google Ditu shows the disputed border areas between China and India as being part of China, while on Google Maps those disputed areas are shown inside dotted lines.
Google Moon[]
Main article: Google Moon

Google Moon
In honor of the 36th anniversary of the Apollo 11 moon landing on July 20, 1969, Google took public domain imagery of the Moon, integrated it into the Google Maps interface, and created a tool called Google Moon.[68] By default this tool, with a reduced set of features, also displays the points of landing of all Apollo spacecraft to land on the Moon. It also included an easter egg, displaying a Swiss cheese design at the highest zoom level, which Google has since removed.[citation needed] A recent collaborative project between NASA Ames Research Center and Google is integrating and improving the data that is used for Google Moon. This is the Planetary Content[69] Project. Google Moon was linked from a special commemorative version of the Google logo displayed at the top of the main Google search page for July 20, 2005 (UTC).[70]
Google Mars[]
Main article: Google Mars

Google Mars
Google Mars provides a visible imagery view, like Google Moon, as well as infrared imagery and shaded relief (elevation) of the planet Mars. Users can toggle between the elevation, visible, and infrared data, in the same manner as switching between map, satellite, and hybrid modes of Google Maps. In collaboration with NASA scientists at the Mars Space Flight Facility located at Arizona State University, Google has provided the public with data collected from two NASA Mars missions, Mars Global Surveyor and 2001 Mars Odyssey.[71]
Now, with Google Earth 5 it is possible to access new improved Google Mars data at a much higher resolution, as well as being able to view the terrain in 3D, and viewing panoramas from various Mars landers in a similar way to Google Street View.
Google Sky[]
Main article: Google Sky
On August 27, 2007, Google introduced Google Sky, an online space mapping tool that allows users to pan through a map of the visible universe, using photographs taken by the Hubble Space Telescope.
Google Ride Finder[]
Google launched an experimental Google Maps-based tool called Ride Finder, tapping into in-car GPS units for a selection of participating taxi and limousine services. The tool displays the current location of all supported vehicles of the participating services in major U.S. cities, including Chicago and San Francisco, on a Google Maps street map. As of 2009[update] the tool seems to be discontinued. Not to be confused with carpooling.
Google Transit[]
In December 2005, Google launched public transport route planner Google Transit on Google Labs, a 20% project of Chris Harrelson and Avichal Garg.[72] Google Transit launched initially with support for Portland, Oregon, and now includes hundreds of cities in the United States, Canada, Europe, Asia, Africa, Australia, India (Pune & Delhi,NCR), and New Zealand. The service calculates route, transit time and cost, and can compare the trip to one using a car. In October 2007 Google Transit graduated from Google Labs and became fully integrated into Google Maps.[73]
The coverage of Google Transit is publicly available. It is spread worldwide, in hundreds of cities and sometimes in entire countries such as China, Japan, Switzerland. The coverage of major cities in the United States and in Canada is almost exhaustive.
In some areas, such as the United Kingdom, Google Transit covers only part of the transit agencies.
In other areas, Google Transit does not provide public transit directions, but still provides the Transit Layer which overlays the schematic of the transit lines on the map. Notable examples include Paris, Berlin, Mexico City and many other capitals around the world.
Google Biking directions[]
On March 10, 2010, Google added the possibility to search for biking directions on Google Maps. Optimal routes are calculated from traffic, elevation change, bike paths, bike lanes, and preferred roads for biking. An optional layer also shows different types of biking paths, from bike-only trails to preferred roads. This service is available in the US[74][75] and Canada,[76] and is in beta testing in some other countries such as Singapore.
Google My Maps[]
In April 2007, My Maps was a new feature added to Google's local search maps. My Maps lets users and businesses create their own map by positioning markers, polylines and polygons onto a map. The interface is a straightforward overlay on the map. A set of eighty-four pre-designed markers is available, ranging from bars and restaurants to webcam and earthquake symbols. Polyline and Polygon color, width and opacity are selectable. Maps modified using My Maps can be saved for later viewing and made public or marked as unlisted, in which case a user will need the saved URL with a 42 character unique ID.
Each element added to a My Map has an editable tag. This tag can contain text, rich text or HTML. Embeddable video and other content can be included within the HTML tag.
Upon the launch of My Maps there was no facility to embed the created maps into a webpage or blog. A few independent websites have now produced tools to let users embed maps and add further functionality to their maps.[77] This has been resolved with version 2.78.[citation needed]
Google Street View[]
Main article: Google Street View
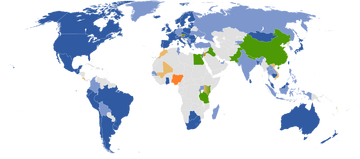
Countries and dependencies with:
coverage in all states/provinces
coverage only in some states/provinces
coverage in all or some states/provinces planned (official)
coverage in all or some states/provinces planned (unofficial)
views of selected businesses and/or tourist attractions only
no current or planned coverage
On May 25, 2007, Google released Street View, a new feature of Google Maps which provides 360° panoramic street-level views of various locations. On this date, the feature only included five cities in the U.S., but it has since expanded to thousands of locations around the world.
In August 2008, Australia was added to the Street View feature with nearly all Australian highways, roads and streets having the feature. In addition in that month Japan was added and the Tour de France route was added on July 2 of that year. In December 2008, New Zealand was added to street view. The United Kingdom, Australia and New Zealand are the only countries to date with almost all roads and highways featured.
July 2009, Google begins mapping college campuses and surrounding paths and trails. Mexico's main cities and tourist points are added to Street View.
Street View garnered much controversy after its release because of privacy concerns about the uncensored nature of the panoramic photographs.[78][79] Since then, Google has begun blurring faces through automatic face detection.[80]
References[]
- ↑ "Google Earth prompts security fears.". ABC News Online. August 8, 2005. http://www.abc.net.au/news/indepth/featureitems/s1432602.htm.
- ↑ "Blurred Out: 51 Things You Aren't Allowed to See on Google Maps". http://www.itsecurity.com/features/51-things-not-on-google-maps-071508/.
- ↑ Google Maps: The White House. "Google Maps: The White House — Elliott C. Back". Elliottback.com. http://elliottback.com/wp/archives/2005/04/08/google-maps-the-white-house/. Retrieved 2010-08-27.
- ↑ Google support forum Clouds over Delhi
- ↑ "Hows does Google Maps work". Techpogo.com. 2009-01-25. http://www.techpogo.com/2009/01/hows-does-google-maps-work.html. Retrieved 2010-01-12.
- ↑ "Blurry or Outdated Imagery". http://earth.google.com/support/bin/answer.py?hl=en&answer=21417.
- ↑ Gautham A. S.. "Google Revises Their Map, Adds Offline Version and 3D Imaging". TechGau.org. http://www.techgau.org/2012/06/google-revises-their-map-adds-offline.html. Retrieved 9 June 2012.
- ↑ "Step inside the map with Google MapsGL". Googleblog.blogspot.com. http://googleblog.blogspot.com/2011/10/step-inside-map-with-google-mapsgl.html. Retrieved 2012-04-25.
- ↑ "Official Google Blog: The world is your JavaScript-enabled oyster". http://googleblog.blogspot.com/2005/06/world-is-your-javascript-enabled_29.html.
- ↑ "Google Maps API – Terms of use". http://www.google.com/apis/maps/terms.html.
- ↑ "Google Geo Developers Blog: Big Birthday... Google Maps API Turns 5!". code.google.com. 2010-05-29. http://googlegeodevelopers.blogspot.com/2010/06/big-birthday-google-maps-api-turns-5.html.
- ↑ "ProgrammableWeb API dashboard". www.programmableweb.com. http://www.programmableweb.com/apis.
- ↑ "Google Maps API FAQ". http://code.google.com/apis/maps/faq.html#tos_commercial.
- ↑ "Google Maps API FAQ Usage Limits". http://code.google.com/apis/maps/faq.html#usagelimits.
- ↑ "Google Maps API Premier". http://www.google.com/enterprise/earthmaps/maps.html.
- ↑ Alan Eustace (September 2, 2011). "A fall spring-clean". Google. http://googleblog.blogspot.com/2011/09/fall-spring-clean.html. Retrieved September 2, 2011.
- ↑ "in-depth review". Mobilitynow.org. 2007-05-08. http://mobilitynow.org/2007/05/08/google-maps-for-mobile-indepth-review/. Retrieved 2010-01-12.
- ↑ "Google Maps on your phone". Google.com. http://www.google.com/mobile/gmm/stp-js.html. Retrieved 2010-01-12.
- ↑ Arrington, Michael (2009-10-28). "Google Redefines GPS Navigation Landscape: Google Maps Navigation For Android 2.0". Techcrunch.com. http://www.techcrunch.com/2009/10/28/google-redefines-car-gps-navigation-google-maps-navigation-android/. Retrieved 2010-01-12.
- ↑ "Google Maps for mobile announce Navigation Beta for Android 2.0 – GSMArena.com news". Gsmarena.com. http://www.gsmarena.com/google_maps_for_mobile_anounce_navigation_beta_for_android_20-news-1216.php. Retrieved 2010-01-12.
- ↑ "Fun on the Autobahn: Google Maps Navigation in 11 more Countries". Googlemobile.blogspot.com. 2010-06-09. http://googlemobile.blogspot.com/2010/06/fun-on-autobahn-google-maps-navigation.html. Retrieved 2011-02-26.
- ↑ "Google VP lays down mobile stats, boasts 150 million Maps users". EnGadget. March 14, 2011. http://www.engadget.com/2011/03/14/google-vp-lays-down-mobile-stats-boasts-150-million-maps-users/.
- ↑ Ito, Keith (2009-10-28). "Blogspot.com". Googleblog.blogspot.com. http://googleblog.blogspot.com/2009/10/announcing-google-maps-navigation-for.html. Retrieved 2010-01-12.
- ↑ Ohazama, Chikai (2011-07-07). ""Download map area" added to Labs in Google Maps for Android - Official Google Mobile Blog". Googlemobile.blogspot.com. http://googlemobile.blogspot.com/2011/07/download-map-area-added-to-labs-in.html. Retrieved 2012-04-25.
- ↑ http://news.cnet.com/Google-mapper-Take-browsers-to-the-limit/2100-1038_3-5808658.html
- ↑ Kiss, Jemima (June 17, 2009). "Secrets of a nimble giant – guardian.co.uk". London: Guardian. http://www.guardian.co.uk/technology/2009/jun/17/google-sergey-brin. Retrieved October 30, 2010.
- ↑ "Google Maps announcement on Google Blog". Googleblog.blogspot.com. http://googleblog.blogspot.com/2005/02/mapping-your-way.html. Retrieved January 12, 2010.
- ↑ "Google Maps Help". Maps.google.com. http://maps.google.com/support/bin/answer.py?answer=16532. Retrieved January 12, 2010.
- ↑ "Google accused of airbrushing Katrina history". msnbc. March 30, 2007. http://www.msnbc.msn.com/id/17880969/.
- ↑ "Google Restores Katrina's Scars To Google Earth". Information Week. April 2, 2007. http://www.informationweek.com/news/internet/search/showArticle.jhtml?articleID=198701867.
- ↑ "Google Mars". Mars.google.com. http://mars.google.com/. Retrieved January 12, 2010.
- ↑ [1][dead link]
- ↑ "Geocoding at Last". http://googlemapsapi.blogspot.com/2006/06/geocoding-at-last.html. Retrieved August 25, 2010.
- ↑ "Google Maps for Enterprise". http://googlemapsapi.blogspot.com/2006/06/google-maps-for-enterprise.html. Retrieved August 25, 2010.
- ↑ "The prodigal son of a search engine comes home". blumenthals.com. http://blumenthals.com/blog/2006/12/28/the-prodigal-son-of-a-search-engine-comes-home/.
- ↑ "New Google UI feature: Plus Box". Matt Cutts. http://www.dullest.com/blog/new-google-ui-feature-plus-box/.
- ↑ "Google Maps With Multiple Destinations". Philipp Lenssen. http://blogoscoped.com/archive/2006-12-19.html#n36.
- ↑ "Google Maps adds subway stops, building outlines to cities". CNET. Archived from the original on 2012-07-11. http://archive.is/eBCO.
- ↑ "Find and Compare Local Businesses". http://googleblog.blogspot.com/2007/01/find-and-compare-local-businesses.html. Retrieved August 25, 1010.
- ↑ "Stuck in Traffic?". http://googleblog.blogspot.com/2007/02/stuck-in-traffic.html. Retrieved August 25, 2010.
- ↑ "Google Upgrades Local Business Center". http://blumenthals.com/blog/2007/03/08/google-upgrades-local-business-center/. Retrieved August 25, 2010.
- ↑ "Local Businesses in Universal Search". http://google-latlong.blogspot.com/2007/05/local-businesses-in-universal-search.html. Retrieved August 25, 2010.
- ↑ "Neighborhood Search Capability". http://google-latlong.blogspot.com/2007/05/posted-by-david-tussey-product-manager.html. Retrieved August 25, 2010.
- ↑ "Driving Directions Support Added to Google Maps". http://googlemapsapi.blogspot.com/2007/05/driving-directions-support-added-to.html. Retrieved August 25, 2010.
- ↑ "Google Maps Launches Street View". http://blumenthals.com/blog/2007/05/29/google-maps-launches-street-view/. Retrieved August 25, 2010.
- ↑ "Add Your Reviews to Businesses on Google Maps". http://google-latlong.blogspot.com/2007/06/add-your-reviews-to-businesses-on.html. Retrieved August 25, 2010.
- ↑ "It's Click and Drag Situation". http://google-latlong.blogspot.com/2007/06/its-click-drag-situation.html. Retrieved August 25, 2010.
- ↑ "Microformats in Google Maps". http://googlemapsapi.blogspot.com/2007/06/microformats-in-google-maps.html. Retrieved August 25, 2010.
- ↑ "Google announces a simple new way to embed Google Maps". http://www.google.com/intl/en/press/annc/embed_maps.html. Retrieved August 25, 2010.
- ↑ "More of the World for You to Explore". http://google-latlong.blogspot.com/2007/09/more-of-world-for-you-to-explore.html. Retrieved August 25, 2010.
- ↑ "Google Transit Graduates from Labs". http://google-latlong.blogspot.com/2007/10/google-transit-graduates-from-labs.html. Retrieved August 25, 2010.
- ↑ "Community Maps in your Search Results". http://google-latlong.blogspot.com/2007/10/community-maps-in-your-search-results_1522.html. Retrieved August 25, 2010.
- ↑ "Google Coupons Now Has Searchable Interface". http://blumenthals.com/blog/2007/10/27/google-coupons-now-has-searchable-interface/. Retrieved August 25, 2010.
- ↑ "Google Maps New Local Onebox 10 Pack Now Live". http://blumenthals.com/blog/2008/01/22/google-maps-new-local-onebox-10-pack-now-live/. Retrieved August 25, 2010.
- ↑ "Google Maps Offers Refine by User Rating Option". http://blumenthals.com/blog/2008/02/20/google-maps-offers-refine-by-user-rating-option/. Retrieved August 25, 2010.
- ↑ "It's Your World, Map It". http://google-latlong.blogspot.com/2008/03/its-your-world-map-it.html. Retrieved August 25, 2010.
- ↑ "Google Local Business Center Upgrade: Unlimited Category Options". http://blumenthals.com/blog/2008/03/19/google-local-business-center-upgrade-unlimited-category-options/. Retrieved August 25, 2010.
- ↑ "Last Summer Somewhere in Adirondacks". http://google-latlong.blogspot.com/2008/04/last-summer-somewhere-in-adirondacks.html. Retrieved August 25, 2010.
- ↑ 59.00 59.01 59.02 59.03 59.04 59.05 59.06 59.07 59.08 59.09 59.10 59.11 "Do you know how many Maps features have been launched in the past 6 months?". Google Maps Water Cooler. January 13, 2009. http://maps-forum-announcements.blogspot.com/2009/01/do-you-know-how-many-maps-features-have.html. Retrieved May 10, 2009.
- ↑ Shankland, Stephen (August 29, 2008). "Google to buy GeoEye satellite imagery | Digital Media – CNET News". News.cnet.com. http://news.cnet.com/8301-1023_3-10028842-93.html. Retrieved January 12, 2010.
- ↑ Chen, Brian X. (October 8, 2008). "Google’s Super Satellite Captures First Image | Wired Science | Wired.com". Blog.wired.com. http://blog.wired.com/wiredscience/2008/10/geoeye-1-super.html. Retrieved January 12, 2010.
- ↑ "New logo look". http://googleblog.blogspot.com/2009/05/new-logo-look.html.
- ↑ "Google Replaces Tele Atlas Data in US with Google StreetView Data". blumenthals.com. October 12, 2009. http://blumenthals.com/blog/2009/10/12/google-replaces-tele-atlas-data-in-us-with-google-data/.
- ↑ "Nu kan du tage bussen med Google Maps i Danmark" (in Danish). http://www.version2.dk/artikel/14959-nu-kan-du-tage-bussen-med-google-maps-i-danmark.
- ↑ Mitchell, Thor (2011-04-08). "Updates to the Google Maps/Google Earth APIs Terms of Service". Googlegeodevelopers.blogspot.com. http://googlegeodevelopers.blogspot.com/2011/04/updates-to-google-maps-apigoogle-earth.html. Retrieved 2012-04-25.
- ↑ "AFP: France convicts Google Maps for unfair competition". Google.com. 2012-02-01. Archived from the original on 2012-02-05. http://web.archive.org/web/20120205155759/http://www.google.com/hostednews/afp/article/ALeqM5hpu8TuRZEBjM30sFn8c7QvMWNjXA?docId=CNG.108b2dd2393721c4759b1eec0730b297.171. Retrieved 2012-04-25.
- ↑ "Zagat goes free with launch of Google+ Local". paidContent. http://paidcontent.org/2012/05/30/zagat-free-google-plus-local/. Retrieved 30 May 2012.
- ↑ "Google Moon". Moon.google.com. http://moon.google.com. Retrieved January 12, 2010.
- ↑ "Intelligent Systems Division | Project". Ti.arc.nasa.gov. http://ti.arc.nasa.gov/tech/asr/intelligent-robotics/planetary/. Retrieved January 12, 2010.
- ↑ "Google". Archived from the original on July 20, 2005. http://web.archive.org/web/20050720082857/http://www.google.com/.
- ↑ "About Google Mars". Google.com. http://www.google.com/mars/about.html. Retrieved January 12, 2010.
- ↑ Chan, Sewell (September 23, 2008). "Google Transit Expands to New York - City Room Blog - NYTimes.com". Cityroom.blogs.nytimes.com. http://cityroom.blogs.nytimes.com/2008/09/23/google-tool-gives-new-york-transit-help/. Retrieved January 12, 2010.
- ↑ "Google LatLong: Google Transit Graduates from Labs". Google-latlong.blogspot.com. October 3, 2007. http://google-latlong.blogspot.com/2007/10/google-transit-graduates-from-labs.html. Retrieved January 12, 2010.
- ↑ Guymon, Shannon. "Biking directions added to Google Maps". Googleblog.blogspot.com. http://googleblog.blogspot.com/2010/03/biking-directions-added-to-google-maps.html. Retrieved 2010-08-27.
- ↑ Leen, John (2010-03-10). "It's time to bike". Google-latlong.blogspot.com. http://google-latlong.blogspot.com/2010/03/its-time-to-bike.html. Retrieved 2010-08-27.
- ↑ Guymon, Shannon (2010-12-01). "Gearing up: Biking directions added to Google Maps for Canada". google-latlong.blogspot.com. http://google-latlong.blogspot.com/2010/12/gearing-up-biking-directions-added-to.html. Retrieved 2011-01-21.
- ↑ "embed my maps – Google Search". Google.co.uk. http://www.google.co.uk/search?q=embed+my+maps. Retrieved January 12, 2010.
- ↑ "The Google 'ick' factor". July 15, 2007. http://ifpandnpthenwe.gnn.tv/headlines/14488/The_Google_ick_factor.
- ↑ Poulsen, Kevin (July 15, 2007). "Want Off Street View?". Wired. http://blog.wired.com/27bstroke6/2007/06/want_off_street.html.
- ↑ "Google begins blurring faces in Street View". CBS Interactive Inc. May 13, 2008. http://news.cnet.com/8301-10784_3-9943140-7.html.







